What is E Waste Management and How to achieve it?
E Waste Management is the technique of collecting the e-waste, recycling, reuse, and disposal it in an environmental friendly manner to minimize its harmful impact on environment and human health. E-Waste management has become a major challenge as it directly affects human health and the environment, and this is happening due to the lack of awareness. The growing problem of E-waste calls for greater emphasis on recycling E-waste and better E-management.
Proper control over the material used in the manufacturing process is important to reduce waste generation (Freeman1989). The quantity of waste generated can be reduced by reducing the number of hazardous materials used in the process and the amount of excess raw materials in stock. This can be done in two ways, i.e., establishing material-purchase review and control procedures and inventory tracking system.
EPR Registration for Manufacturers and Importers
The government passed the first law in 2011, based on Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), which makes the manufacturer liable for managing the final stage of the life of its product in an eco-friendly way and ensures environmentally sound management. An Extended Producer's Responsibility (EPR) certificate or license is mandatory for every producer/importer producing electric or electrical equipment. It encourages manufacturers to produce environment-friendly products. EPR Authorization is issued by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) under MoEFCC, Government of India.
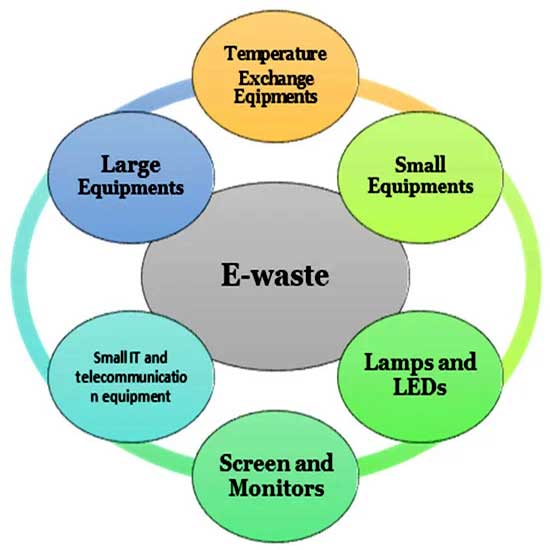
As per the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016, all the manufacturers of Electrical and Electronics (EEE) products/equipments listed in schedule 1 are responsible for collecting, recycling and disposing the final stage of their EEE product from an authorized dismantler/recycler. As per the guidelines, manufacturers, and importers needs to tie-up with the authorized recycler to dispose of the E-Waste and submit all the plans related to the estimated dump quantity and method adopted for disposal in CPCB to get the EPR Certificate. In short, the product's manufacturer is responsible for the product's ultimate recycling, reuse, or disposal.
EPR - E-Waste (Management) Rules 2022
The Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change issued E-Waste (Management) Rules 2022 on November 2, 2022. This will go into effect on April 1, 2023.
As per this regulation, all manufacturers, producers, refurbishers, and recyclers shall have to register on the portal and collect e-waste generated during the manufacturing, refurbishing, or disposal of any electrical and electronic equipment and ensure its recycling or disposal. The Entities must register on the portal under the appropriate category, such as manufacturer, producer, refurbisher, or recycler. If an entity falls into more than one category, it must register under each category separately. It is illegal for any entity to conduct business without registration.
- All entities shall have to file annual and quarterly returns in the prescribed form on the portal on or before the end of the month following the quarter or year to which the return relates.
- These regulations shall apply to all manufacturers, producers, refurbishers, dismantlers, and recyclers engaged in the manufacture, sale, transfer, purchase, refurbishment, dismantling, recycling, and processing of e-waste or electrical and electronic equipment listed in Schedule I.
- The Central Pollution Control Board may charge registration fees and annual maintenance fees on entities seeking registration under these rules based on the capacity of e-waste generated, recycled or handled by them, as determined by the Central Pollution Control Board with the approval of the Steering Committee.
- The producer of electrical and electronic equipment listed in Schedule I must first register on the portal to obtain and implement extended producer responsibility targets as per Schedule III and IV.
Benefits of EPR Registration Certificate
- EPR promotes the recycling and reuse of the e-waste (Electrical and electronics waste), hence reduces the cost of raw material for the producers/manufacturers.
- EPR ensures the management of e-waste in environmentally friendly manner, hence reduce the harmful impact of e-waste on environment.
- EPR Authorization from Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) enhance the goodwill of the product and brand reputation in the market.
- EPR promotes sustainable development, hence lowers the waste generation and misuse of the natural resources.